Megaloblastic Anemia Treatment. The anemia is corrected with thiamine treatment, but the red cells remain macrocytic, and anemia can recur when treatment is withdrawn. The diagnosis is based on a general blood test, a smear of peripheral blood, in which macrocytic anemia with anisocytosis and poikilocytosis is determined, large oval red blood cells.
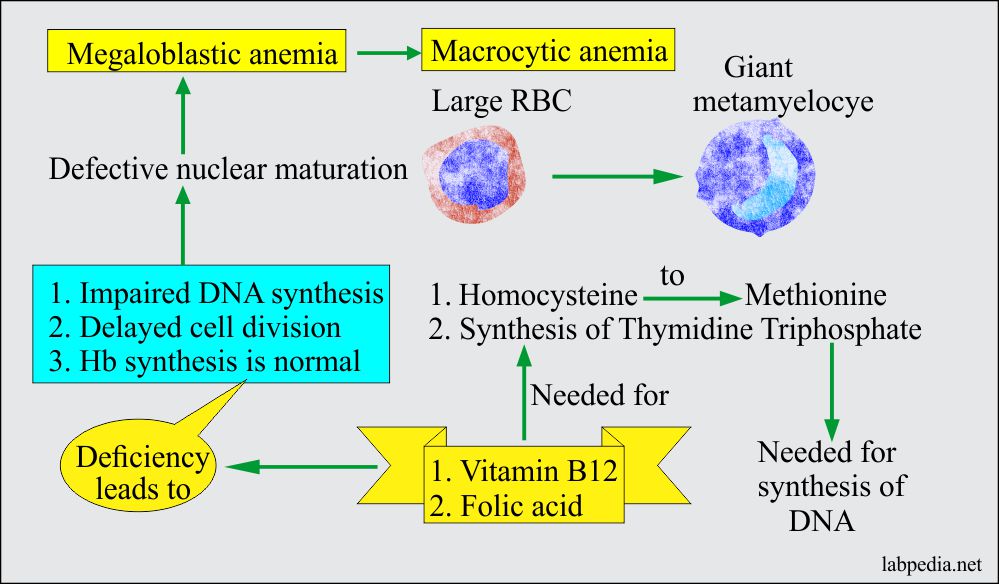
The anemia is corrected with thiamine treatment, but the red cells remain macrocytic, and anemia can recur when treatment is withdrawn. The diagnosis is based on a general blood test, a smear of peripheral blood, in which macrocytic anemia with anisocytosis and poikilocytosis is determined, large oval red blood cells. Vitamin b 12 deficiency anemia and folate deficiency anemia often occur together and can be hard to tell apart. Megaloblastic and nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemias. Megaloblastic anemia is caused by deficiency or impaired utilization of vitamin b12 and/or folate, whereas nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia is caused by various diseases such as myelodysplastic syndrome (mds), liver dysfunction, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, certain drugs, and by less commonly inherited disorders of dna synthesis.
Dietary changes also help boost folate levels.
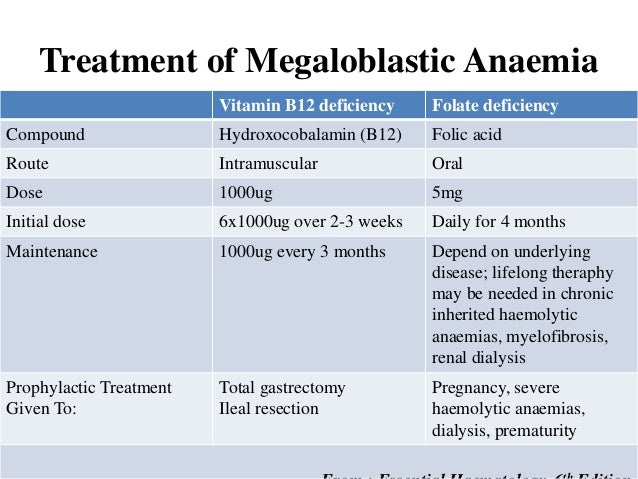
Folinic acid is also effective in the treatment of folate deficient megaloblastic anaemia but it is generally used in association with cytotoxic drugs; Treatment may include vitamin b 12 shots (injections) and folic acid pills. Decreased levels of folate or vitamin b12 are the most reliable criteria of megaloblastic anemia. Megaloblastic anemia is caused by deficiency or impaired utilization of vitamin b12 and/or folate, whereas nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia is caused by various diseases such as myelodysplastic syndrome (mds), liver dysfunction, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, certain drugs, and by less commonly inherited disorders of dna synthesis. Treatment with vitamin b12 results in sustained clinical improvement of the anemia and resolution of the neurologic symptoms, if present. Injections of vitamin b12 once a month. Megaloblastic anemia is the result of a deficiency of vitamin b 12 and folic acid. Foods that are rich in folic acid include the following: Vitamin b 12 deficiency anemia and folate deficiency anemia often occur together and can be hard to tell apart. However, other benign and neoplastic diseases need to be considered. There is no justification for prescribing multiple ingredient vitamin preparations containing vitamin b 12 or folic acid. With these available in advance, therapy with the appropriate vitamin can be begun at once. These include celiac disease, chronic infectious enteritis, and enteroenteric fistulas.
Treatment with vitamin b12 results in sustained clinical improvement of the anemia and resolution of the neurologic symptoms, if present. The diagnosis is based on a general blood test, a smear of peripheral blood, in which macrocytic anemia with anisocytosis and poikilocytosis is determined, large oval red blood cells. Most macrocytic anemias are also megaloblastic. Replacing any nutritional deficiencies through changes in diet. Megaloblastic anemia can be diagnosed based on characteristic morphologic and laboratory findings.
The most common causes are folate (vitamin b9) deficiency and cobalamin (vitamin b12) deficiency.
Macrocytic anemia can be broken into two main types: Most macrocytic anemias are also megaloblastic. The treatment of megaloblastic anemia depends on the specific cause, as well as other factors like your age, overall health, severity of disease, and your response to treatment. Treating the specific deficiency of vitamins forms the mainstay. The anemia is corrected with thiamine treatment, but the red cells remain macrocytic, and anemia can recur when treatment is withdrawn. Dietary changes also help boost folate levels. Treatment with vitamin b12 results in sustained clinical improvement of the anemia and resolution of the neurologic symptoms, if present. Megaloblastic anemia can be diagnosed based on characteristic morphologic and laboratory findings. Megaloblastic anemia causes macrocytic anemia from ineffective red blood cell production and intramedullary hemolysis. More foods to incorporate into your. Ineffective hematopoiesis affects all cell lines, but in particular erythroid. Of course, your child's team of doctors will help determine the best approach. Transfusions are rarely required in patients with a megaloblastic anemia that is due to vitamin b12 deficiency.
Ineffective hematopoiesis affects all cell lines, but in particular erythroid. Replacing any nutritional deficiencies through changes in diet. These include celiac disease, chronic infectious enteritis, and enteroenteric fistulas. Most macrocytic anemias are also megaloblastic. There is no justification for prescribing multiple ingredient vitamin preparations containing vitamin b 12 or folic acid.
Treatment may include vitamin b 12 shots (injections) and folic acid pills.
Treating the specific deficiency of vitamins forms the mainstay. Dietary insufficiency of cobalamin and folate can be treated with appropriate changes to the diet and the administration of supplements. Treatment of megaloblastic anemia is tailored according to the underlying cause. If serum levels are unavailable or available only in retrospect, initial treatment, especially of severe anemia, should be with both vitamins. The anemia is corrected with thiamine treatment, but the red cells remain macrocytic, and anemia can recur when treatment is withdrawn. Macrocytic anemia can be broken into two main types: Pernicious anemia is a type of megaloblastic anemia. Defective nucleoprotein synthesis resulting in the development of megaloblastic anemia was described for the first time more than 50 years ago by victor herbert 7. Of course, your child's team of doctors will help determine the best approach. There are many causes of megaloblastic anemia. Treatment the treatment of megaloblastic anemia depends upon the underlying cause of the disorder. Possibly addressing the absorption problem in the digestive tract. Anemia due to megaloblastic anemia is usually reticulocytopenic.

Tidak ada komentar: